With the help of Java operators, we can perform mathematical or logical operations on different data types.
Types
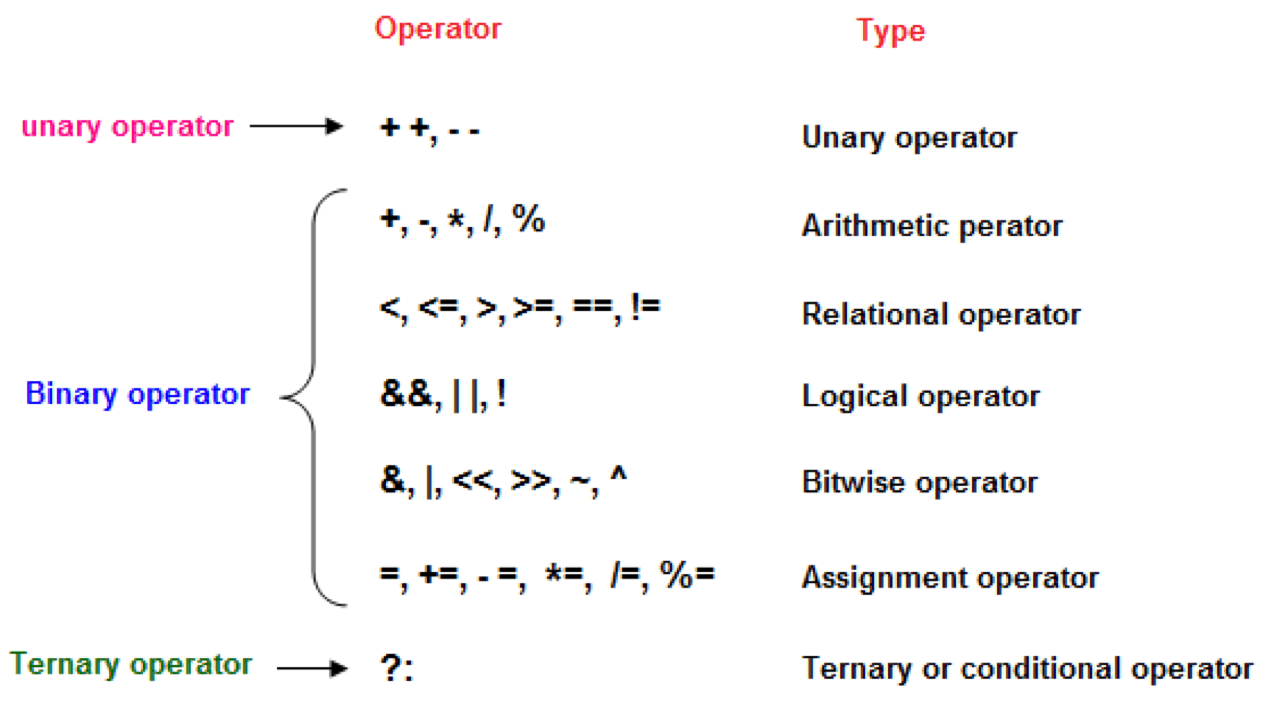
Explanation –
Code sample –
Arithmetic operator –
public class ArithOp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 13;
int b = 5;
int result;
result = a % b;
System.out.println(result);
}
}
Output – 3
Assignment operator –
public class AssignOp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 6;
a += 5; // a= a+5 ~ a=6+5
System.out.println(a);
}
}
Output – 11
Bitwise operator –
public class BitwiseOp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 6;
int b = 8;
int result = a | b;
System.out.println(result);
}
}
Output – 14
Conditional operator –
public class CondOp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int result;
int a = 8;
int b = 7;
result = (a < b) ? (a+b) : (a-b); //cond? true : false
System.out.println(result);
}
}
Output – 1
Logical operator –
public class LogicalOp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean Andresult = (2<3) && (3!=3); //true && false
System.out.println(Andresult);
boolean ORresult = (3<5) || (3!=4);
System.out.println(ORresult);
boolean negResult = !(true);
System.out.println(negResult);
}
}
Output –
false
true
false
Relational operator –
public class RelationalOp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 4;
int b = 4;
//boolean result = (4 != 8);
boolean result = (a == b);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
Output – true
Unary Operator –
public class UnaryOp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 7;
//int result = a++; //result = a; a = a+1;
a--; //a = a-1
//System.out.println(result);
System.out.println(a);
}
}
Output – 6
— Notes —
Logical operator
&&
any one side is false., then result is false
true && false = false
true && true = true
false && false = false
———————-
||
any one side is true. result is true
true || false = true
true || true = true
false || false = false
—————
!
!(true) = false
!(false) = true
Bitwise operator
& – if any one side is 0, then result is 0
6 = 0110
8 = 1000
result = 0000 = 0
| – if any one of the side is 1, then result is 1
6 = 0110
8 = 1000
1110 = 14