Inheritance
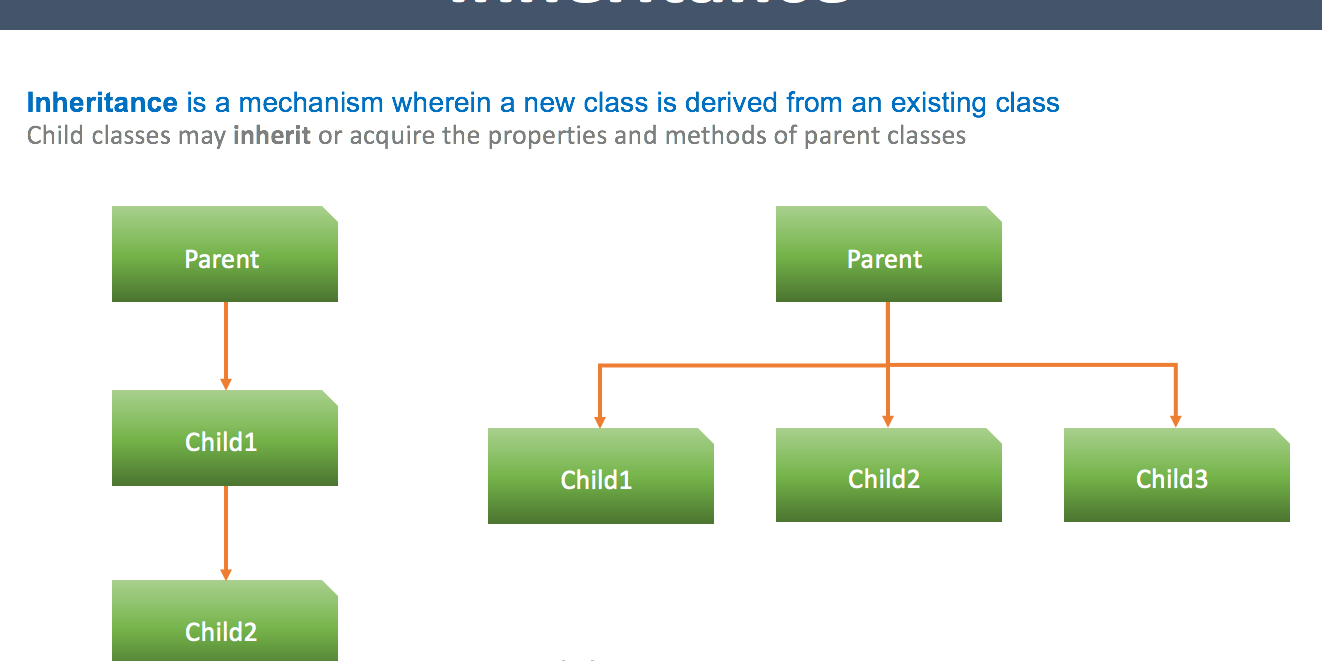
Inheritance is a mechanism wherein a new class (child class) is derived from an existing class (parent class), child classes may inherit or acquire the properties and methods of parent classes.
Types of inheritance
- Single / multi level inheritance
- Hierarchical inheritance
Benefits of inheritance
- Reusability
- Extensibility
- Saves time and effort
- Provides clear model structure
For details, watch here
Code samples
Example – 1
Base Class – Animals
—-Child Class – Cat
—-Child Class – Lion
——–Child Class – Cub
package inheritanceEx;
public class Animals {
int NoOfEyes = 2;
Animals(){
System.out.println("Animals : -");
}
public void Eat() {
System.out.println("I can eat");
}
public void Eyes() {
System.out.println("I have "+ NoOfEyes + " eyes");
}
}
package inheritanceEx;
public class Cat extends Animals{
void Meow() {
System.out.println("Sound of cat - Meow");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cat cat = new Cat();
cat.Eat();
cat.Eyes();
cat.Meow();
}
}
package inheritanceEx;
public class Lion extends Animals{
void Roar() {
System.out.println("Sound of lion - Roar");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Lion lion = new Lion();
lion.Eat();
lion.Eyes();
lion.Roar();
//lion.Meow(); //no relation between cat and lion
}
}
package inheritanceEx;
public class Cub extends Lion{
void Cooing() {
System.out.println("Sound of Cub - Coo");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cub cub = new Cub();
//super(); //error - should be 1st line of the method
cub.Eat();
cub.Eyes();
cub.Cooing();
}
}
//super() - refers to parent constructor
Example – 2
Base Class – BankAcc
—-Child Class – SavingsAcc
——–Child Class – Transactions
package inheritanceEx1;
public class BankAcc {
String Cust_Name;
int CustAcc_No;
BankAcc(String Name, int AccNo){
Cust_Name = Name;
CustAcc_No = AccNo;
}
void DispCust() {
System.out.println("Customer Name - " + Cust_Name);
System.out.println("Customer Acc No - " + CustAcc_No);
}
}
package inheritanceEx1;
public class SavingsAcc extends BankAcc{
int Balance;
int Min_Balance = 1000;
SavingsAcc(String Name, int AccNo, int Bal){
super(Name, AccNo); // BankAcc(String Name, int AccNo){ from BankAcc
Balance = Bal;
}
String isMinBalMaintained() {
if(Balance > Min_Balance) {
return "Yes";
}
else
return "No";
}
void DispCust() {
super.DispCust();
System.out.println("Balance - " + Balance);
System.out.println("Is Min Balance Maintained? - " + isMinBalMaintained());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SavingsAcc savingacc = new SavingsAcc("SKP", 4317625, 23400);
savingacc.DispCust();
}
}
package inheritanceEx1;
public class Transactions extends SavingsAcc{
int Withdrawl;
int Deposit;
Transactions(String Name, int AccNo, int Bal, int exp, int deposit){
super(Name, AccNo, Bal);
Withdrawl = exp;
Deposit = deposit;
Balance += deposit;
Balance -= exp;
}
void DispCust() {
super.DispCust();
System.out.println("Total Withdrawls - " + Withdrawl);
System.out.println("Total Deposits - " + Deposit);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Transactions trans = new Transactions("SKP", 7642398, 23400, 1200, 3400);
trans.DispCust();
}
}