xpath is xml path language, and selenium uses xpath as one of the locator strategies to locate web element[s] from the DOM (document object model).
DOM is nothing but the tree structure of the html / xml document.
xpath normally provides the path to navigate to the required element from the tree structure.
xpath types : Absolute & Relative
Difference between Absolute and Relative xpaths.
Absolute xpath:
Need to provide complete path of the required web element, starting from the root element.
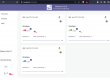
Example: gmail sign in page… find the Email field
As you can see, each tag is separated by a “/”, means they are immediate element to each other.
This is sometimes risky to use, as in real time web applications, the DOM structure changes frequently or if some elements in DOM changed on the way from root to desired element, then absolute xpath will not work.
But in case, where there is no specific attributes to locate the element such as id/name, then we can use the absolute xpath (may be the last solution to locate)…
Relative xpath:
Path can start from any element near on the DOM that are close to the desired element, good practice to chose the near by element (of desired element) which can be uniquely identify on the DOM so we can traverse from there to the desired element easily.
Now xpath will find it’s own easiest way to navigate to the near by element and follows our written path to get to the desired element.
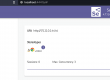
Example: Go to the URL:
Demo Let’s say that the “Full Name” text box and this doesn’t have any unique identifier, it’s just a div element
but we have the field placed on a “Form” (we can identify this by id),
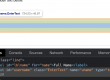
so the xpath is:
Either .//*[@id=’form1′]/fieldset/div[1] or .//form[@id=’form1′]/fieldset/div[1]
Let’s understand this:
.// selects current node
@id=’form1′ – all element attributes are precedent by a sign @ and value in between single quote.
.//[@id=’form1′] finds the occurrence of an element with “id=form1” (* stands for any kind of element input/h1/table/form tags etc), then normal absolute path follows like fieldset and then the 1st div element where Full Name textBox resides.
//form[@id=’form1′] will only look for a tag named form with id=’form1′


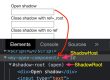
Absolute Path
1.The Path Which Locate the WebElement from Root Node To Required Child Node ,FireFox and Chrome Browser By default generates a Absolute Xpath or CSS Path .
2.Need to update Xpath while Change or removal of any Element from Root Node To Child Node.
3. Low Efficiency as compare to Relative xpath
Relative Path:
1.The Path Which Locate the WebElement from Required Root Node To Required Child Node.
2.Very rare chances to update xpath
3. High Efficiency as compare to Absolute xpath